|
?
?
 |
ustom
Molded Parts
Design
|
? |
Mold Design Considerations
?
Though rubber can be molded into complex shapes, custom-molded rubber parts require specific design and manufacturing considerations. It’s important to find solutions for applications needing close-tolerance molding and assembly.
?
DOIT Rubber Products' extensive expertise in the production process, materials, and technical knowledge allows us to provide design recommendations and deliver reliable products.
|
| Project | Description |
| High-precision Equipment | DOIT has first-class precision CNC and EDM processing equipment both at home and abroad, and the mold processing precision level is stable and reliable. |
| Mold Material Selection | Based on factors such as the product type, structure, surface requirements, and product life cycle required by customers, DOIT evaluates and selects different types of steel. Available materials include S50C, P20, 718, NAK80, S136H, etc. |
| Mold Template Calibration | Before mold opening, both the front and back sides of all new templates will be ground using a high-precision water grinding machine to ensure the parallelism of both sides of the mold and the mold clamping accuracy after mold pressing. |
| Shrinkage Management | DOIT has established a complete database of shrinkage rates for various rubber materials. Based on this, the mold opening size is carefully controlled to ensure that the product meets the drawing tolerance requirements and improves the CPK level of product dimensions. |
| Mold design capability |
DOIT can design and manufacture the following major types of mold processing:
1. Precision molding molds (O-RING, Y-type ring, X-type ring, gasket, etc.)
2. Injection molds
3. Continuous transfer molds
4. Liquid silicone rubber molds
|
| Expertise Type | DOIT is particularly good at high-precision O-RING molding molds, especially automotive O-RING molds. The product appearance, flash ability, mold clamping line precision, and dimensional precision are better than similar products in Europe and the United States. |
| DOIT Advantages |
1. Designing and manufacturing molds independently, with controllable quality and delivery time, and emergency response capability better than the industry.
2. Mold designers have 10-20 years of rich design experience, with a high success rate, reducing test costs.
3. The mold cost is low, and maintenance is convenient. The replication mold after obtaining the customer's consent can be invested in by itself.
4. All templates use big-brand steel with reliable supply and stable quality.
5. Mold opening equipment is updated and calibrated in a timely manner, with stable and reliable precision.
6. It has the ability to develop and process various types of molds, with diverse technical capabilities, and can undertake the ability to develop various products for customers.
7.Proficient in operating various CAD, CAM, and CAE application software for mold design and manufacturing, including Mastercam, UG, and Pro/ENGINEER.
|
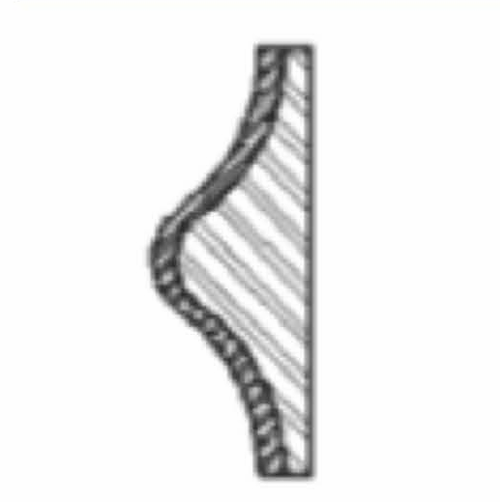
| An undercut is a part feature that projects back into its main body. Deeper undercuts make the part harder or even impossible to remove from the mold. Such molds are expensive to build and run, leading to higher costs. |
Easy Removal
 Side View
Lower Mold Price
|
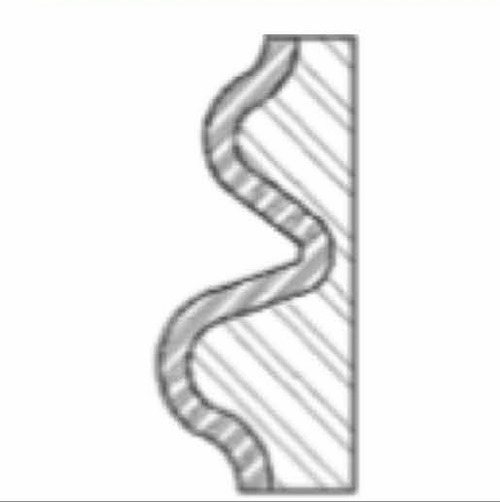
Difficult Removal
 Side View
Higher Mold Price
|
|
Radius Corners
Top View
?
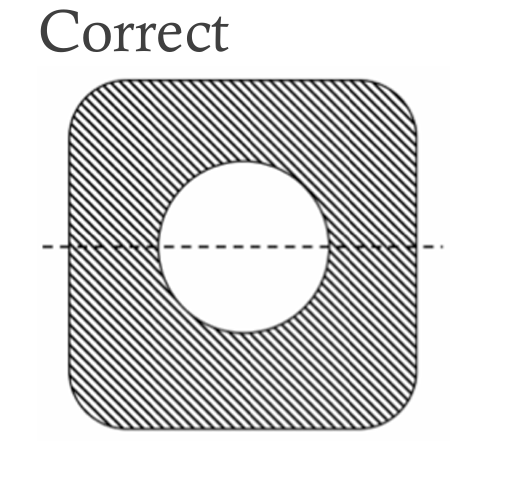 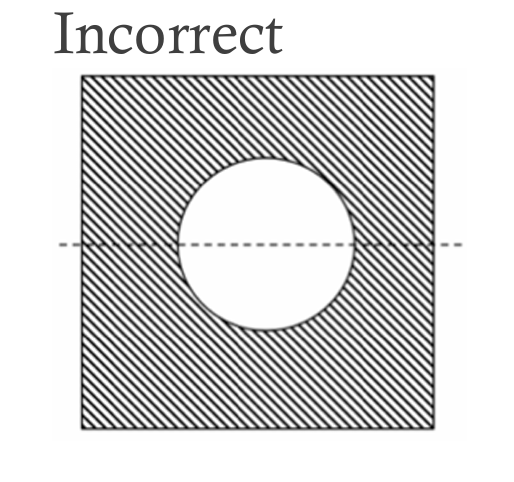 Steel molds are easier to machine with rounded corners than square ones. Sharp corners make machining harder and costlier, and may cause molding defects, harming quality. Thus, parts should have round corners when viewed from above.
|
Square Edges
Side View
?
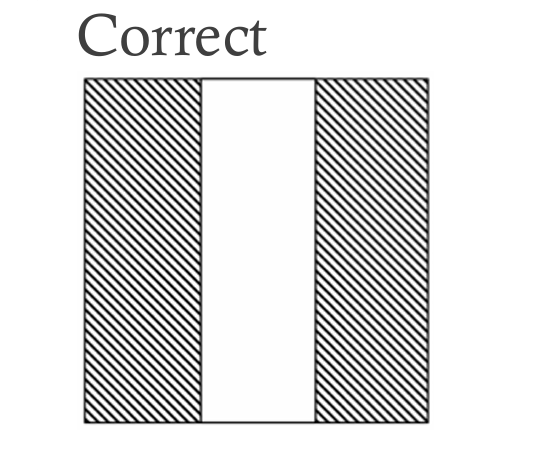 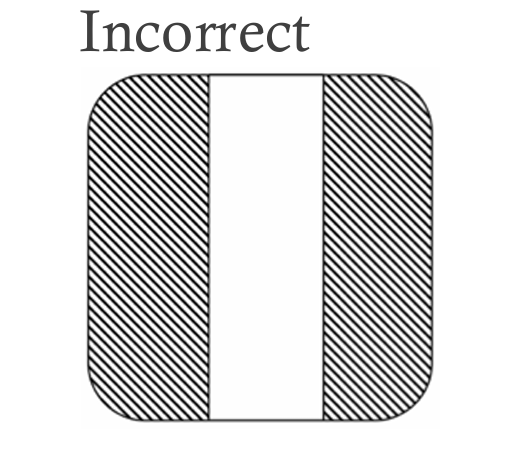 |
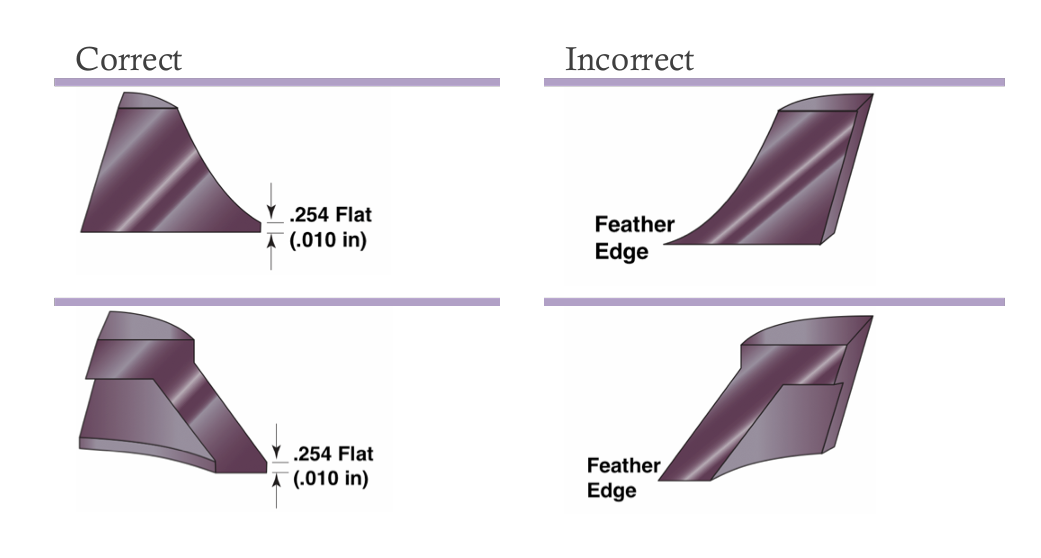
| Sharp edges—also called knife edges or feather edges—tend to tear when removed from the mold and may chip during normal deflashing. So unless sharp edges are necessary, squaring them off (minimum 0.25 mm or .01 in) is recommended. |
 |
|
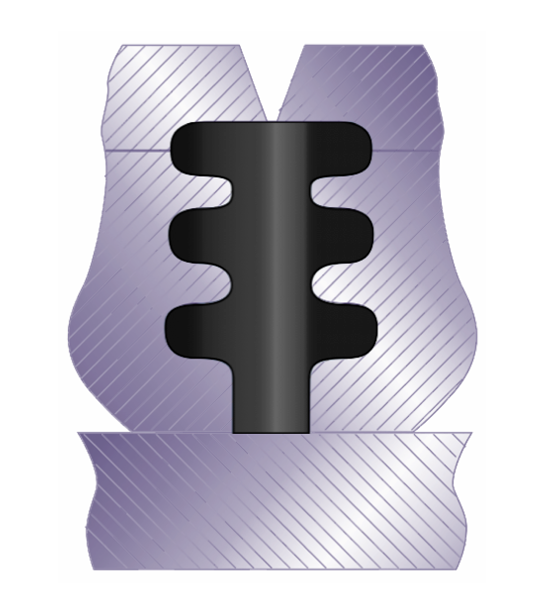
Vertically
?
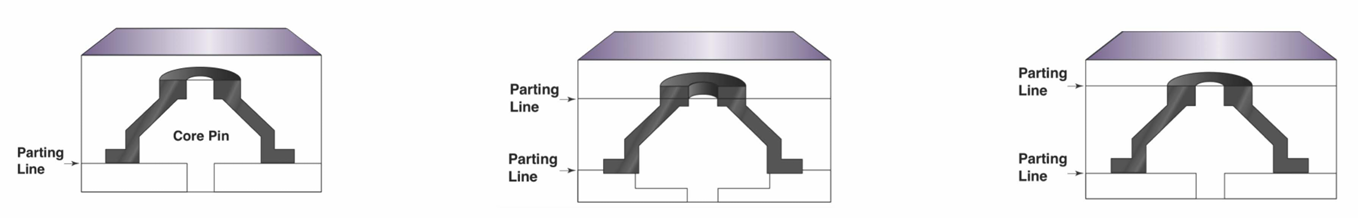
When designing a mold, the removal of the part from a mold should also be considered. For example, the mold (right), composed of three plates, opens vertically. In this case, it would not be possible to remove the part from a horizontally opening mold.
|
 |
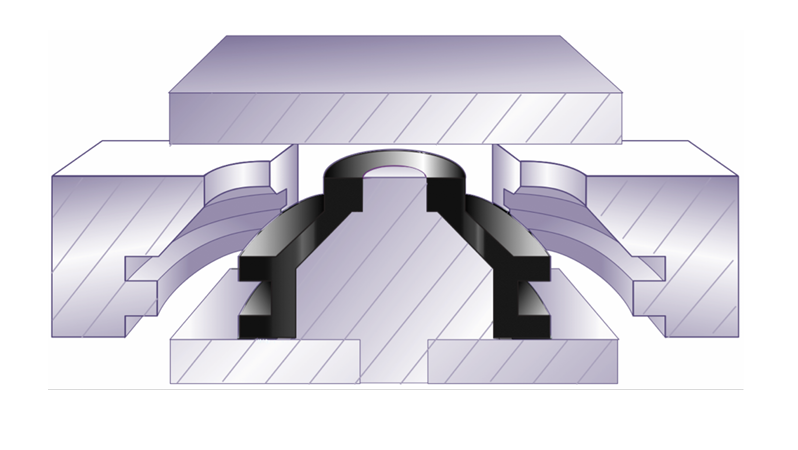
Horizontally and Vertically
?
The mold (right), composed of four plates, opens horizontally as well as vertically. It is easier to take out the part in this design than trying to pull the undercut feature through the center hole.
|
 |
|
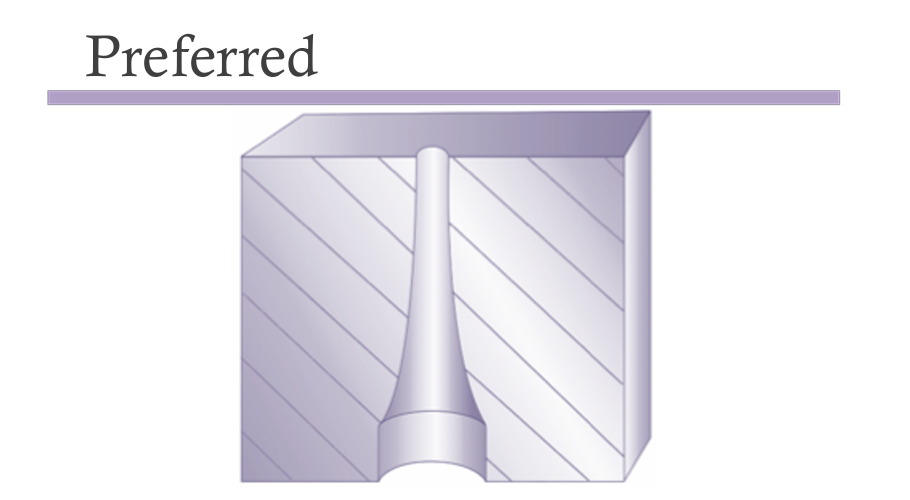
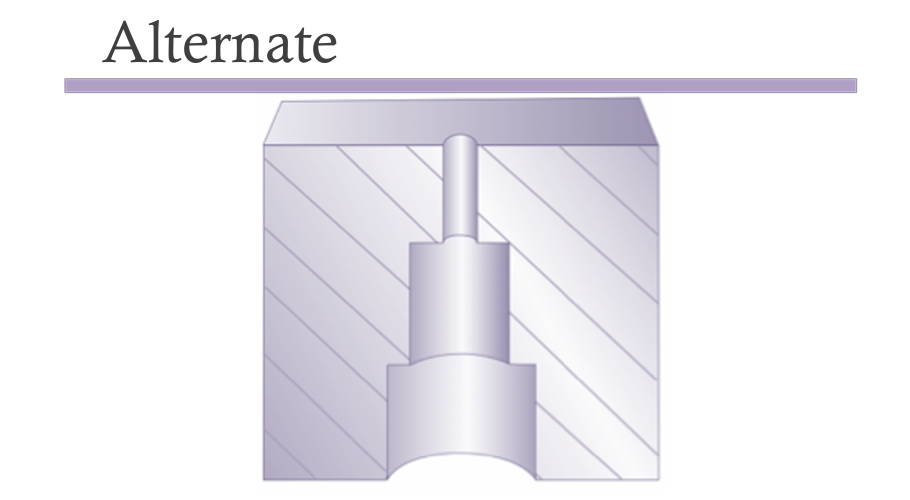
Holes or inner diameters are formed by inserting a core pin into the cavity. High molding pressure can exert strong forces on the pin, possibly bending it and causing irregular holes. Thus, core pin size and hole inner diameter should be maximized (especially at the base) to prevent pin bending or breaking.
?
Basic guidelines are:
-The height of the hole should not be more than twice its diameter
-The minimum diameter of a hole should be about 1.27mm (.050 in)
|
   |
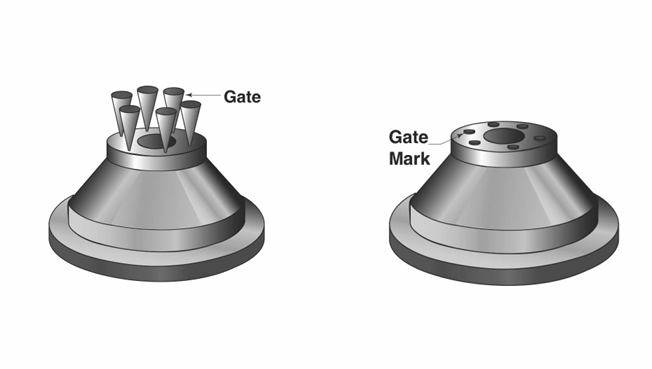
| Transfer and injection molds usually have multiple gates to ensure even material flow into the cavity. These gates, 0.010-0.150 in in diameter, are spaced alon the cavity's circumference. The finished part has a gate mark (a raised spot or small depression).? |
 |








