|
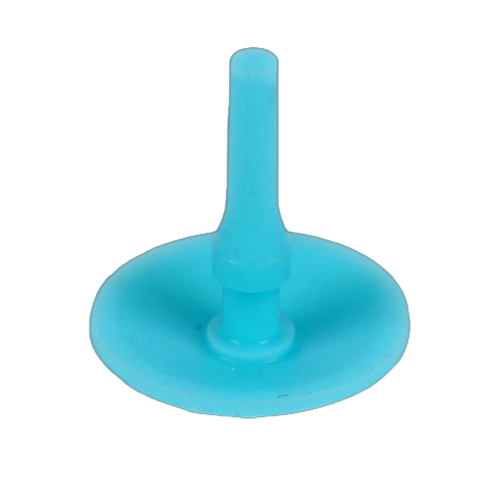
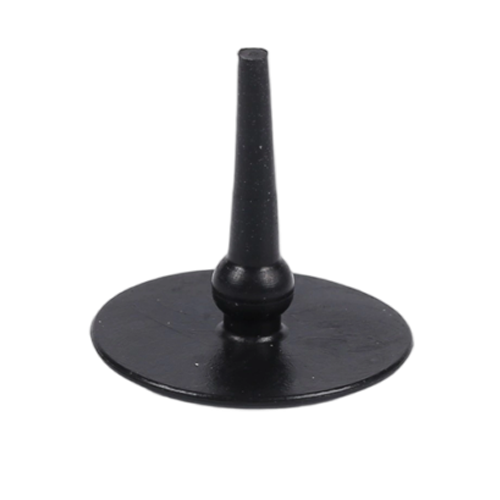
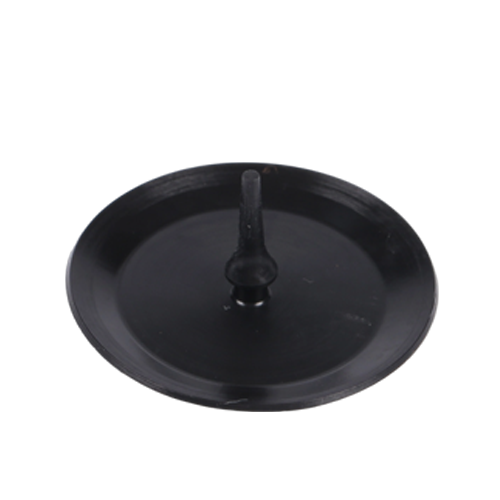
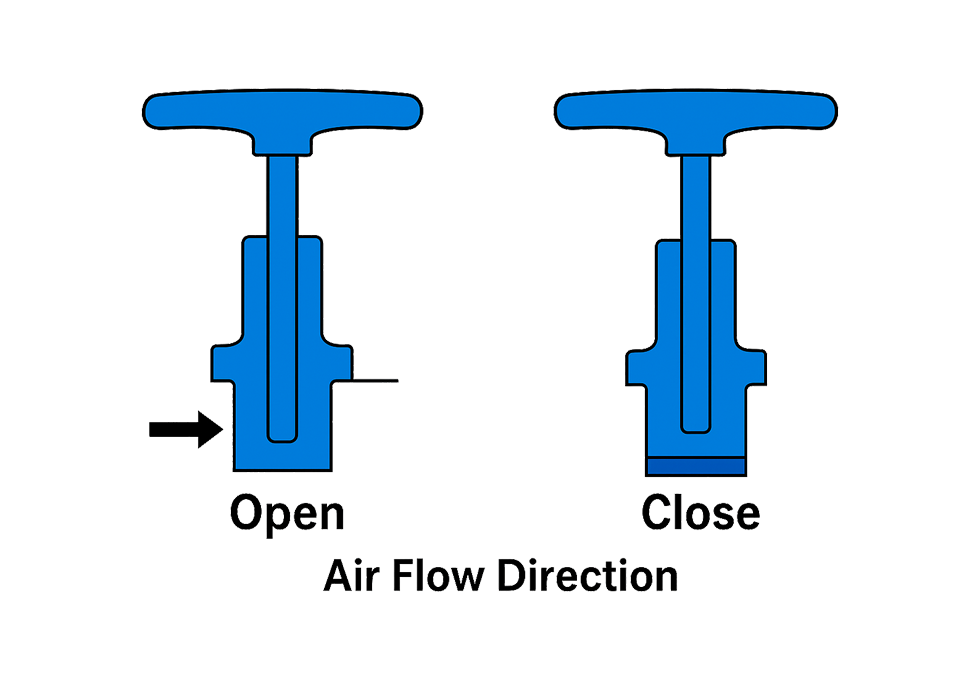
The umbrella valve is a key component of fluid transportation and unidirectional control equipment (such as micro pumps, solenoid valves, medical infusion devices, etc.). It achieves unidirectional fluid conduction and pressure regulation through its own opening and closing, and is widely used in medical, automotive, industrial automation and other fields.
Its performance directly determines the three core aspects:
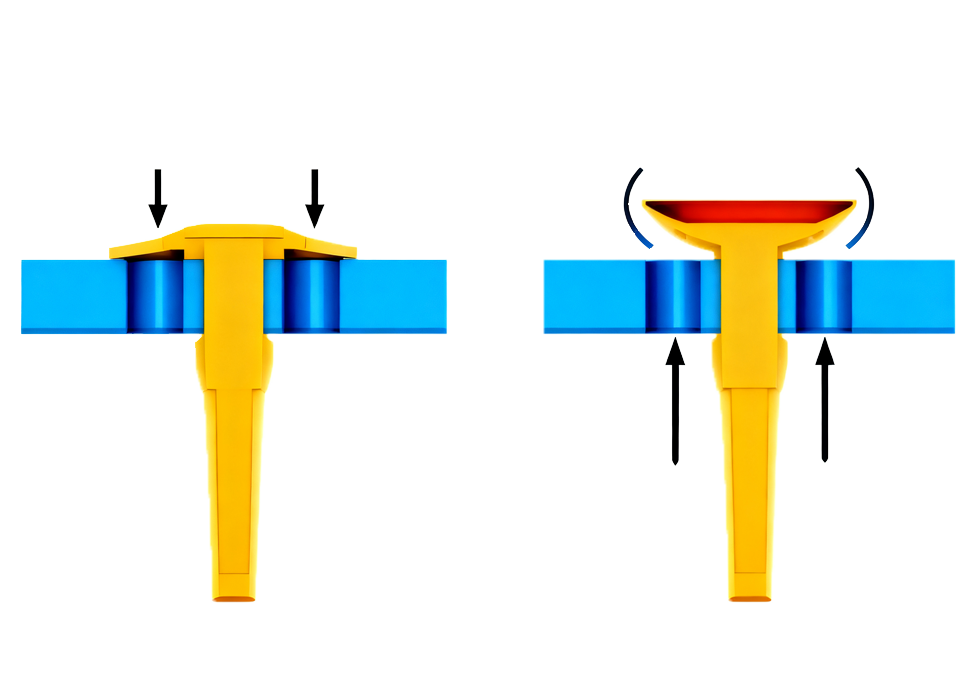
① The reliability of equipment sealing. The structural integrity of the umbrella valve can prevent reverse fluid leakage and ensure the accuracy of transportation;
② Fluid control stability: The appropriate hardness and elasticity can ensure smooth opening and closing, reducing pressure fluctuations.
③ Equipment maintenance cost: High-quality umbrella valves are wear-resistant and deformable, which can reduce the downtime for replacement caused by component failure and extend the overall service life of the equipment. Therefore, the umbrella valve is an important guarantee for the efficient and safe operation of fluid systems.
|
 |
 |
1. Issues with the automatic assembly of the product
Product column deformation: It leads to a decline in assembly accuracy, making it impossible to precisely connect with other components, which may cause subsequent functional abnormalities and increase rework costs. ?
Product column breakage: It directly causes assembly interruption, increases the scrap rate, and at the same time, the residue from the breakage may pollute the assembly environment and affect the efficiency of the production line. ?
The product column is too short to hold: This makes it impossible for automatic assembly to stably fix the workpiece, requiring manual intervention and adjustment, which significantly reduces the production capacity of the assembly line. ?
Product adhesion between products: This leads to difficulties in picking up parts and chaotic sorting, not only slowing down the assembly pace but also potentially causing product damage due to forced separation. ?
2. Functional issues regarding product usage
Excessive or insufficient flow: It fails to meet the precise requirements of the equipment for fluid delivery volume, such as in scenarios like medical liquid infusion and industrial reagent proportioning, which can easily lead to process deviations or functional failures. ?
High product noise: Abnormal sounds are produced during operation, polluting the working environment. At the same time, it indicates that there are structural or performance defects in the product, which may shorten its service life. ?
Product swelling: Due to the penetration of the medium, the size and performance change, leading to seal failure, opening and closing jamming, and subsequently causing fluid leakage or equipment failure. ?
Product deformation without rebound: Losing the core elastic function, unable to normally achieve unidirectional conduction and pressure control, directly leading to the scrapping of the umbrella valve and equipment shutdown.
|
|
Automatic assembly issues: ① Column deformation/breakage/too short: Unreasonable production process parameters (such as injection molding temperature, pressure), column size design deviation, insufficient strength of material formula, or poor compatibility between automatic equipment parameters and products; ② Product adhesion: Improper design of the surface texture of the product makes it prone to mutual adhesion after molding. ?
Functional issues in use: ① Flow deviation: The material hardness is too high or too low, the strength is insufficient, and the production process parameters (such as vulcanization, cooling) fluctuate greatly, resulting in inconsistent performance of products in the same batch; ② High noise: The product wall thickness is too thick, or the material hardness is too low. After being compressed, the cavity expands, and abnormal friction is caused by the dimensional variation of the plastic parts. ③ Product swelling: The material formula is not suitable for the medium in use and is easily dissolved or permeated by the fluid. ④ Deformation without rebound: Physical property design flaws in the material formula, insufficient elastic recovery capacity.
|
|
Solve the problem of automatic assembly: ① Analyze the specific positions where the column deforms, breaks or is too short, and correct the column size to match the design of the plastic parts; ② Optimize production process parameters (such as adjusting injection pressure and cooling time) to enhance the strength of the material formula; ③ For product adhesion, optimize the surface texture design or add anti-adhesion surface treatment; ④ Calibrate the parameters of the automatic equipment to ensure they are compatible with the products. ?
Solve the problem of flow deviation: ① Based on the measured flow data, precisely adjust the material hardness to match the equipment conveying requirements; ② Establish a full-process parameter control system to reduce parameter fluctuations in injection molding, vulcanization and other links, and ensure the consistency of product performance within the same batch. ?
To solve the problem of excessive noise: ① If the wall thickness is too thick, optimize the product structure to reduce the wall thickness; ② If the hardness is too low or the size of the plastic part varies, increase the hardness of the material or correct the dimensional accuracy of the plastic part to reduce abnormal friction. ?
Solve the problem of product swelling: Re-evaluate the characteristics of the medium used, and replace the material formula with one that is resistant to dissolution and permeability to avoid the risk of swelling from the source. ?
Solve the problem of deformation without rebound: ① Increase the hardness of the material to enhance its elastic recovery capacity; ② Observe the movement Angle of the diaphragm through dynamic detection equipment, optimize the design of the plastic swing frame, reduce the swing amplitude, and minimize deformation loss. ?
Environmental compliance guarantee: For the medical, food and other fields, we customize special formulas that comply with environmental protection standards of various countries (such as RoHS, REACH), and produce them in environmentally controlled workshops to eliminate harmful substances and ensure product access qualifications.
|













